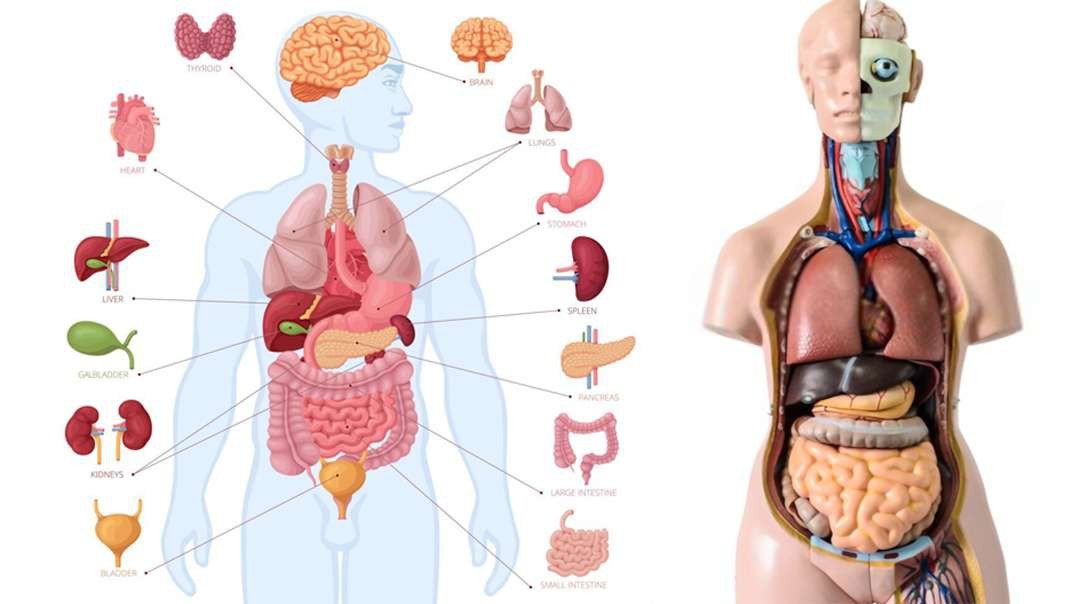
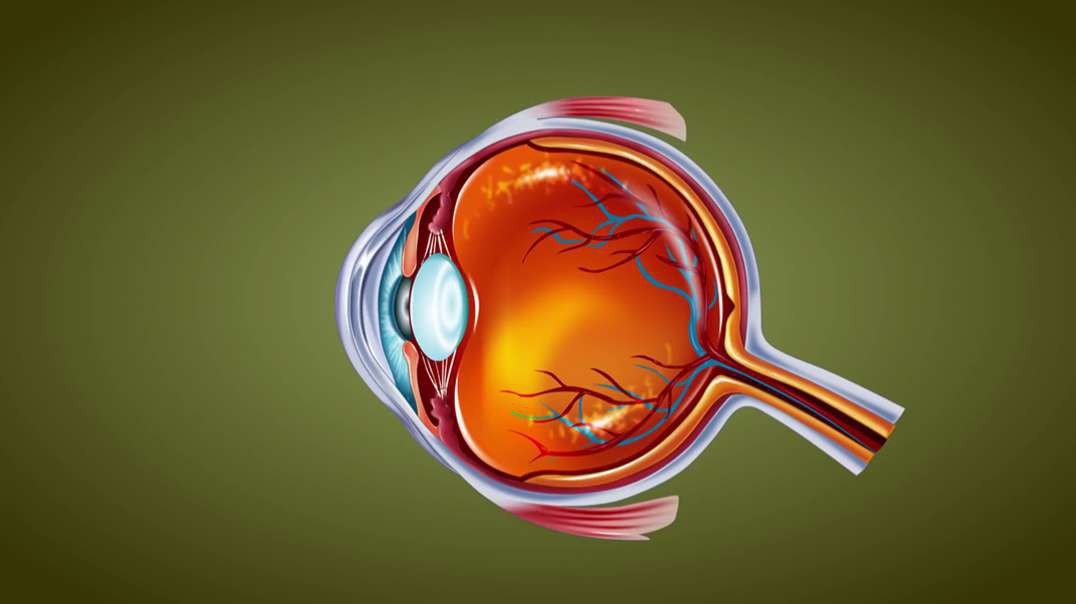
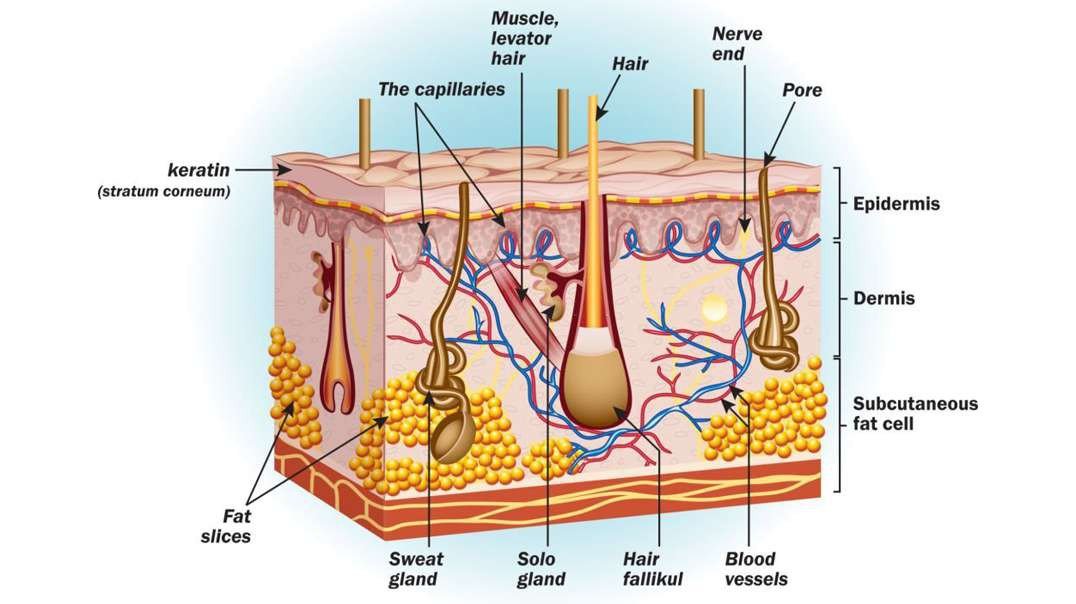
:
Human Eye: Structure and Function
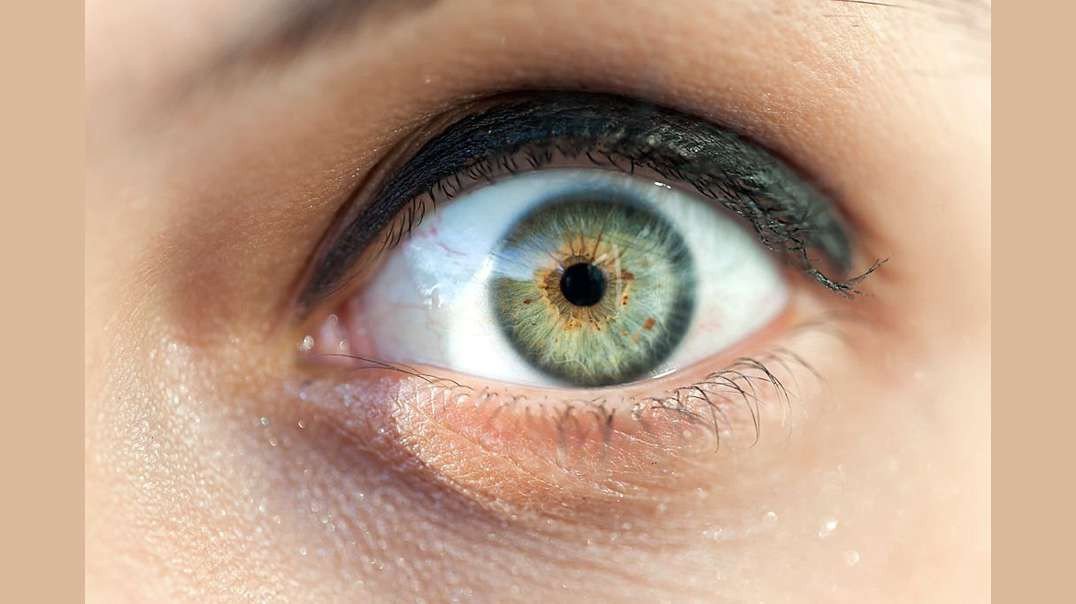
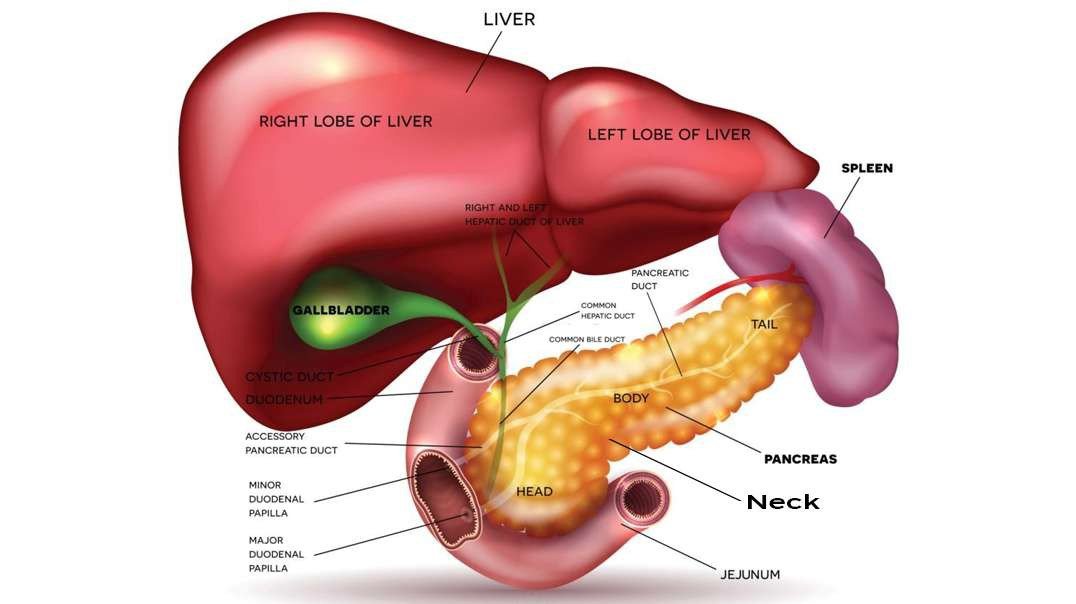
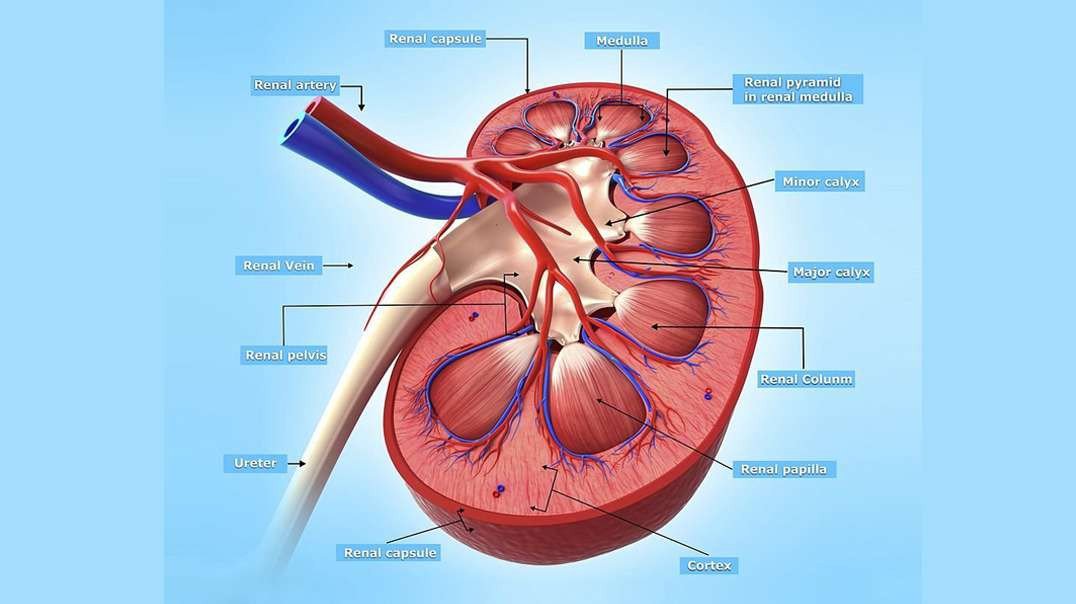
Human eye is a Specialized organ which has ability to receive visual images. If we talk about the horizontal cross section of human eye than we come across that human eye is composed of three layers of tissues. The outermost layer is fibrous layer that consists of sclera and cornea. Sclera is the white part of the eye that helps in maintaining the shape of the eye. Cornea is convex shaped and helps in refraction of light rays which are entering into the eyes. The middle layer of human eye is vascular in nature due to the presence of blood vessels. Middle layer contains choroid, ciliary bodies and iris. The color of choroid is chocolate deep brown. When light enters the eye it stimulates the sensory receptors of retina and then absorbed into the choroid. Ciliary bodies contain ciliary muscles and anteriorly continuous with choroid. Lens is also attached with ciliary bodies with the help of suspensory ligament. Epithelial cells are also present in ciliary bodies. Epithelial cell helps in secretion. Middle layer contains iris which is the visible part of the eye. Iris have different colors in different people. Iris is present behind the cornea and in front of the lens. Iris divides the anterior segment of the eye into anterior and posterior chamber. Iris is circular in shape and have pigments. These pigments impart color to iris. There is an aperture present in the Centre of iris called as pupil. Light rays are entered into the eye through pupil. The color of iris is dependent on the pigment present in it. There is no pigment in the eyes of albinos. The people with blue eyes have very less amount of pigments in it. Lens is very important part of the eye. Thickness of the lens is controlled by ciliary muscles of the eye. The inner layer is made up of nervous tissue consisting of retina. Retina is the most delicate structure of eye. Light sensitive retina contain some cells called as rod and con cells. Some pigments of rod and con cells convert light rays into the nerve impulse. The nerve impulse is than sent to the brain. If we discuss about the blood supply of our eye, oxygenated blood is supplied through ciliary arteries and central retinal arteries. Deoxygenated blood of eye is drained through the veins which include central retinal vein etc. light enters into the eye through cornea which is present in front of the iris and pupil. Cornea acts as a protective covering if the eye. After passing through cornea, light is passed through pupil. Pupil is present in the middle of the eye. Iris, surrounding the pupil controls the amount of light entering into the eye. Ehen the environment is darker; iris allows more light for entrance. When the environment of surrounding is lighter, iris allows less light for entrance. posterior to the iris, lens is present. By changing its shape lens focuses light rays into the retina. Through the action of ciliary muscles, lens changes its shape. To focus near objects lens become thicker and to focus far objects lens become thinner. After passing through the lens, light rays focuses into the retina. The, most sensitive part of retina is macula that contains millions of con cells in it. Due to the high density of con cells in macula, we are able to see detailed visual images. The photoreceptors present in retina converts image into electrical signal. These signals are send to the brain through the optic nerve. The function of con cells is identification of colors and visualization of objects. Rod cells are responsible for night vision and peripheral vision. Rod cells are more in number than con cells and more sensitive to the light. If we will divide the eyeball into two sections than there is fluid in each segment of the eye. This fluid generates pressure which maintains the shape of the eyeball. These fluids are called as aqueous humor and vitreous humor. Aqueous humor nourishes internal structures of the eye and vitreous humor is the jelly like fluid.