:
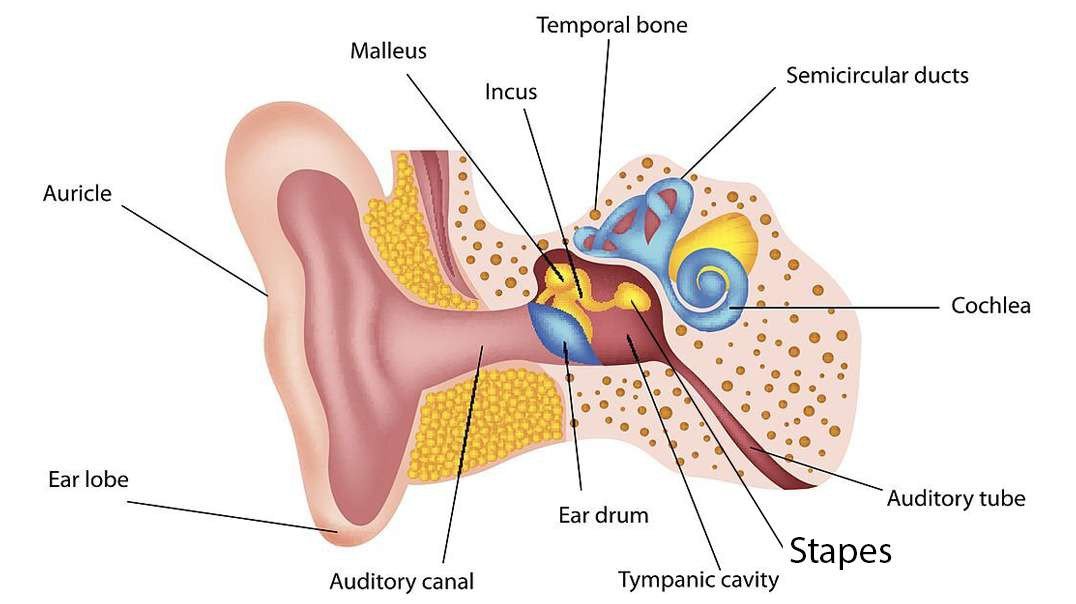
Inner Ear Anatomy
Inner ear Anatomy: Cochlear component, Vestibular component, Semi-circular component - Animation
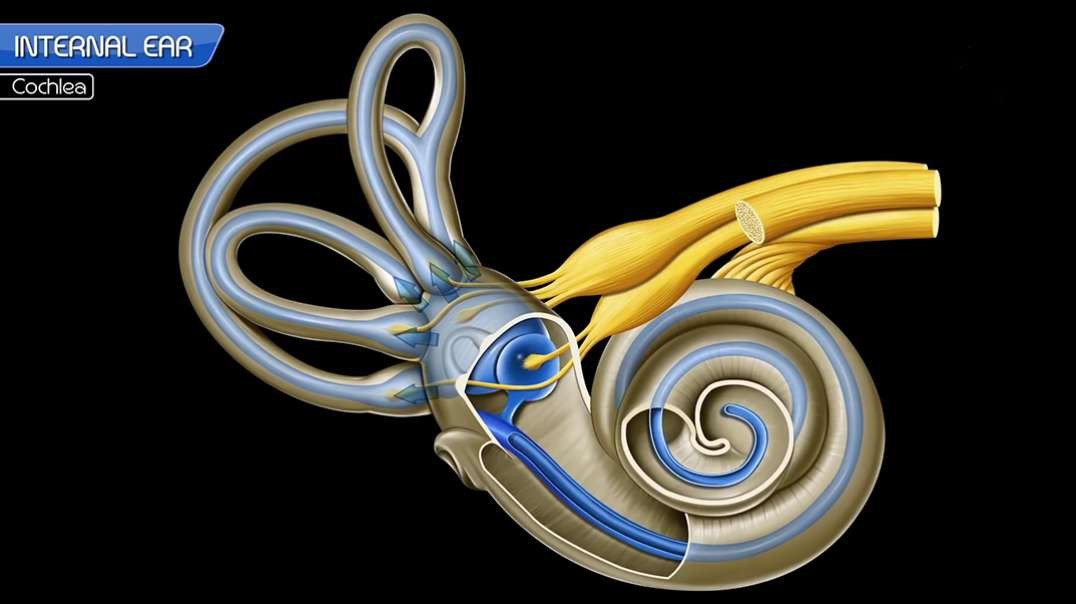
The structures of the inner ear are designed to convert the mechanical energy transmitted in the form of waves generated by surrounding objects into neuronal impulses (transduction) that can be interpreted as sound. Likewise, the inner ear also plays pivotal roles in maintaining postural balance and visual focus on a single object (gaze fixation). As a result, the inner ear (which consists of a series of interlinked cavities termed labyrinths) can be divided into three general parts:
Cochlear component that is concerned with hearing.
Vestibular component (comprised of the utricle and saccule) that deals with balance while stationary.
A semi-circular component that regulates balance while in motion.
The former is located anterior to the latter. The gross anatomical structures, their spatial relations, innervation, and blood supply will be discussed in this article.