:
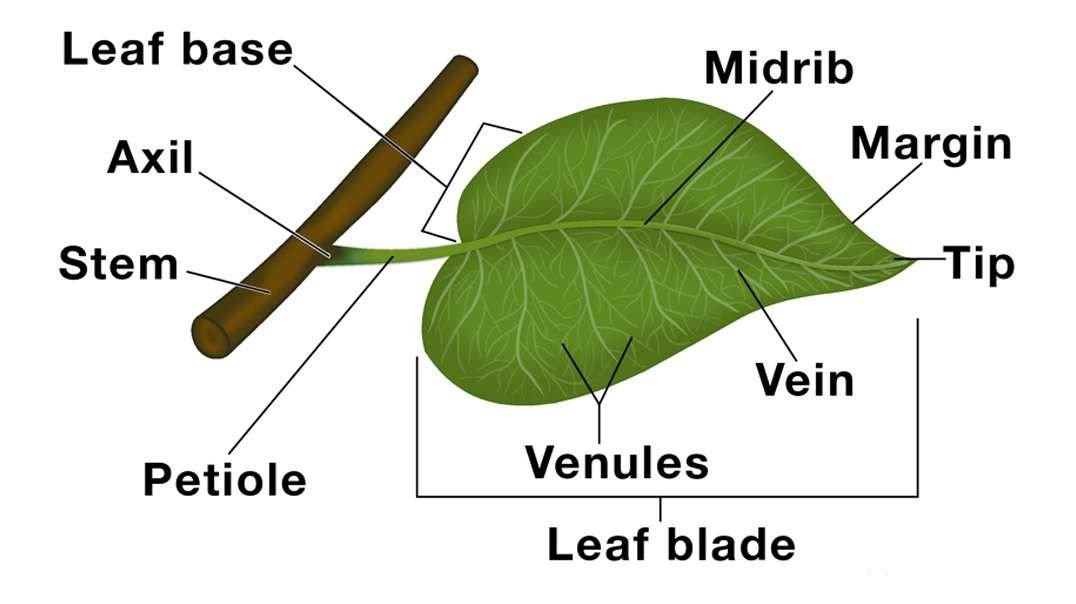
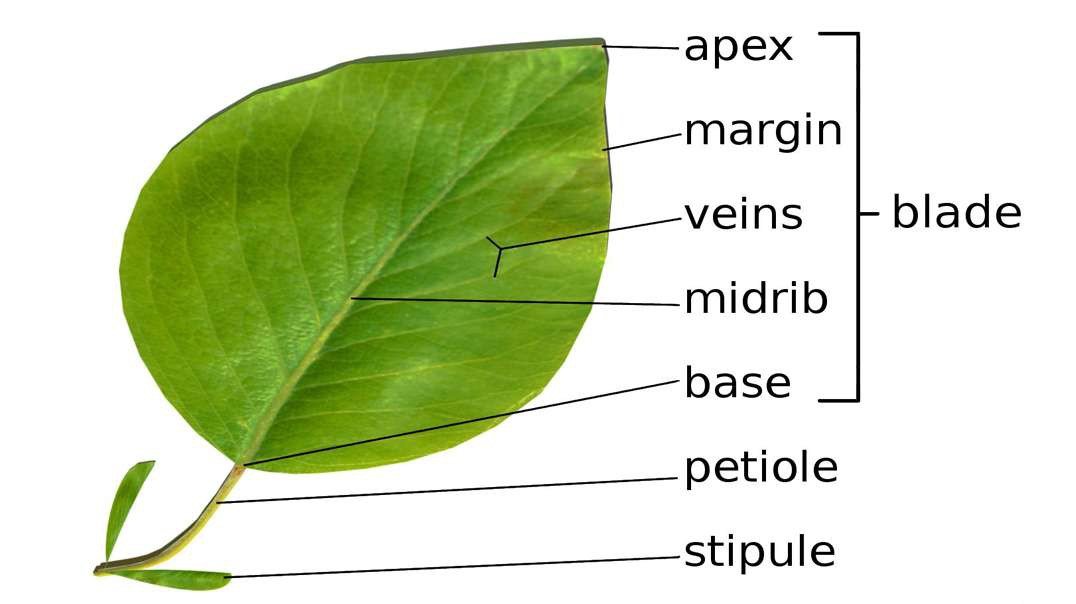
Venation of leaf
VENATION:
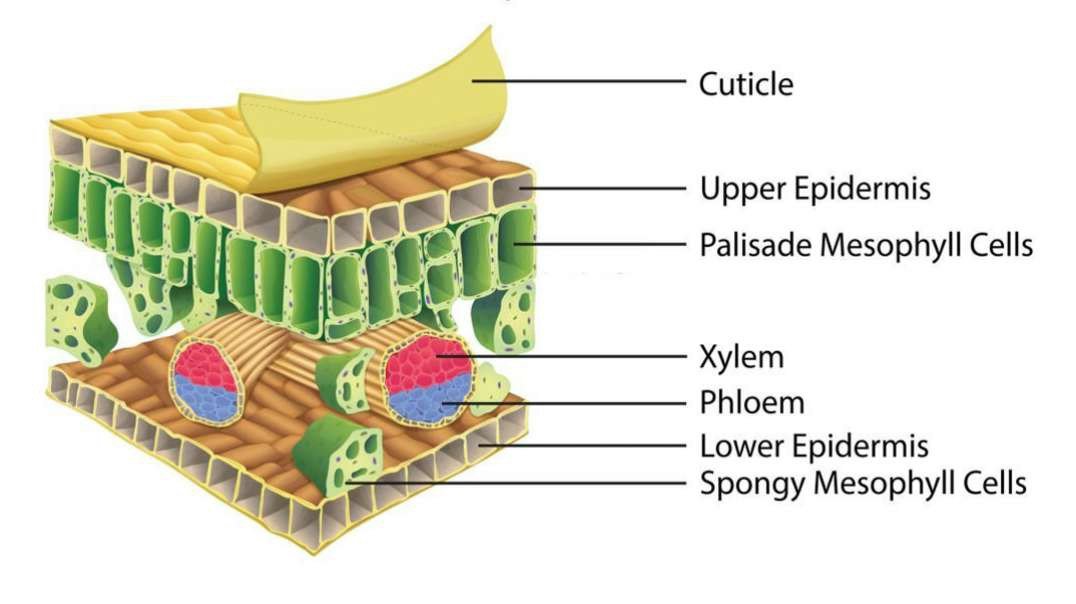
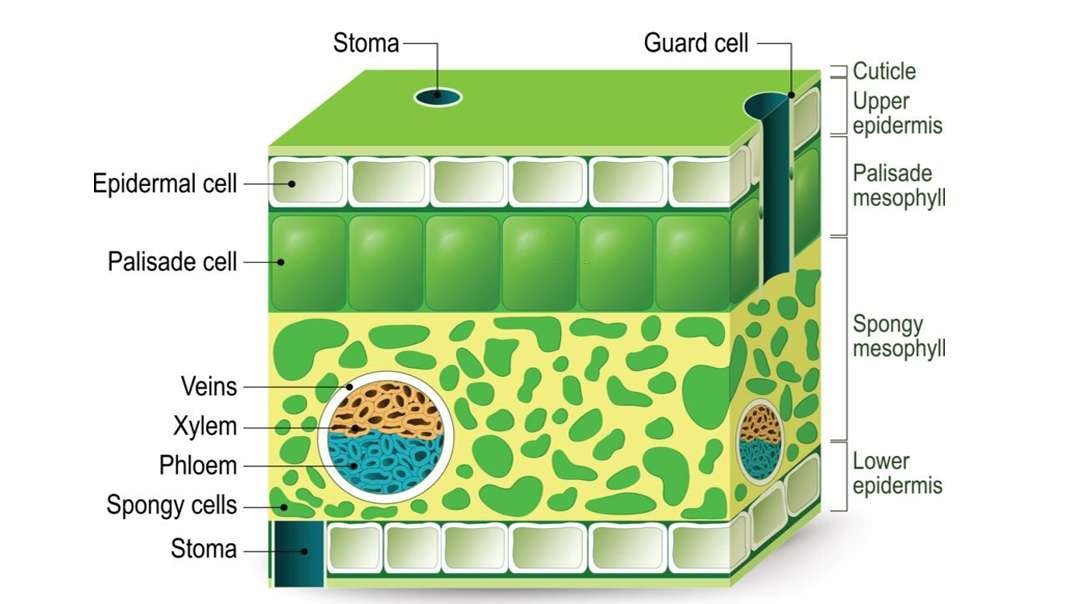
The method of arrangement of veins and veinlets in the leaf lamina of the leaf is called Venation.
Venation provides definite shape and strength to the leaf lamina
It is also concerned with the expansion of the leaf lamina to get a sufficient amount of sunlight.
It helps in the transportation of water, minerals, and food materials.
TYPES OF VENATION:
In angiosperms, the venation is of two types.
They are 1. Reticulate venation and 2. Parallel venation.
RETICULATE VENATION:
The presence of all veins in the leaf lamina in the form of a network is called Reticulate venation.
It is found mainly in dicots.
The monocots with reticulate venation are Smilax and Dioscorea.
Based on the number of midribs, reticulate venation is of two types,
pinnate reticulate and b Palmate reticulate venation.
PINNATE RETICULATE VENATION:
In the leaf lamina, only one midrib is present, all the veins are present in the form of a network is called PINNATE RETICULATE VENATION.
It is also called UNICOSTATE RETICULATE VENATION.
It is the most common type of venation.
Example: Mangifera.
PALMATE RETICULATE VENATION:
In the leaf lamina, more than one midrib is present, and all the veins are arranged in the form of a network, which is called PALMATE RETICULATE VENATION.
It is also called MULTICOSTATE RETICULATE VENATION.
It is classified into two types
1 Convergent and 2 Divergent.
1CONVERGENT -- The leaf lamina is unlobed, all the midveins are run throughout the leaf lamina and meet at the apex.
Example: Ziziphus.
2DIVERGENT -- The leaf lamina is lobbed, and all the midveins enter into their respective lobes.
Examples: Passiflora, Gossypium, Cucurbita
PARALLEL VENATION:
The arrangement of all veins in the leaf lamina parallel with one another is called PARALLEL VENATION
It is mainly found in monocotyledons.
The dicots with parallel venation are Eryngium and Caulophyllum.
Based on the number of midveins, parallel venation is of two types,
1 Pinnate parallel venation and 2 Palmate parallel venation.
PINNATE PARALLEL VENATION:
In the leaf lamina, only one mid vein is present from base to apex, and many parallel veins are produced towards the margins.
It is also called UNICOSTATE PARALLEL VENATION.
Example: Musa paradisiaca.
PALMATE PARALLEL VENATION:
In the leaf many prominent veins are present, and are parallel with one another, is called PALMATE PARALLEL VENATION.
It is also called MULTICOSTATE PARALLEL VENATION.
It is classified into two types:
CONVERGENT --The leaf lamina is unlobed, all the midveins arise from the basal part, run parallel to each other, and unite at the apex.
It is found in the family POACEAE.
Example: Oryza sativa.
DIVERGENT -- The leaf lamina is lobbed, all the veins arise from the base and enter into the lobes separately.