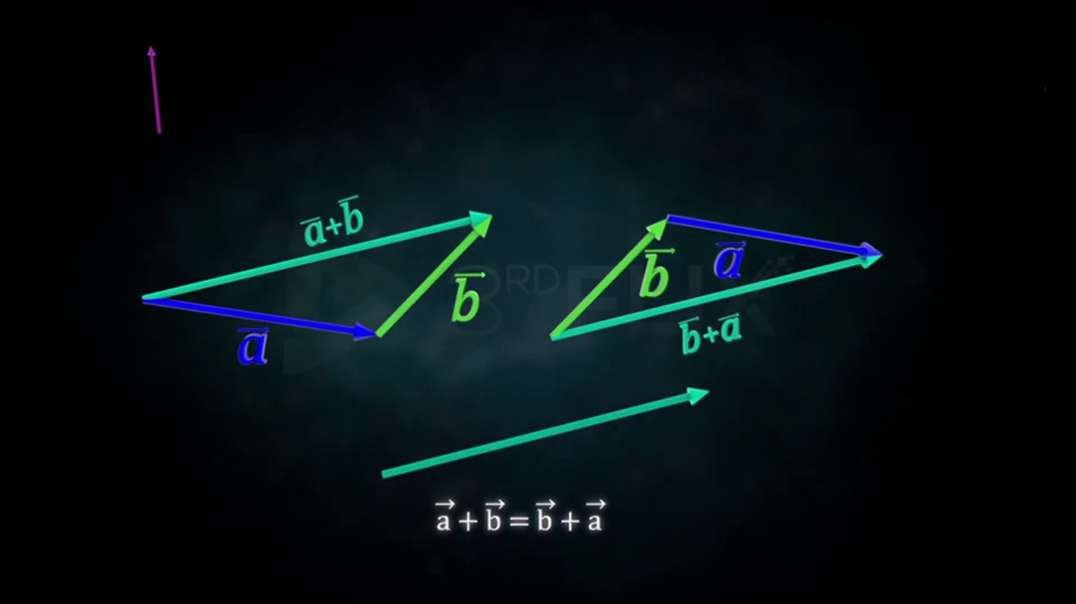
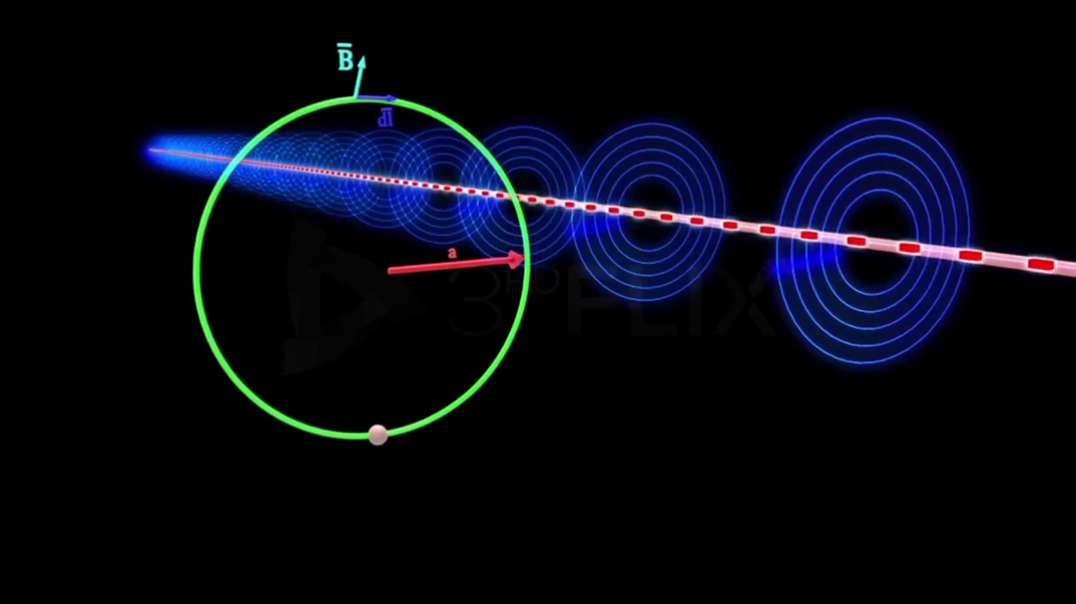
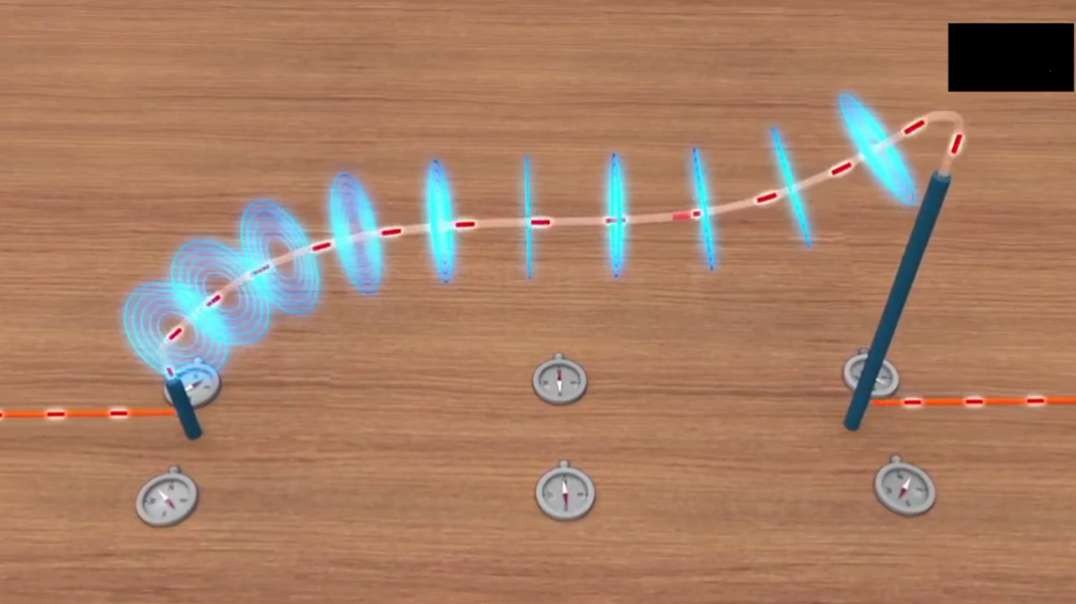
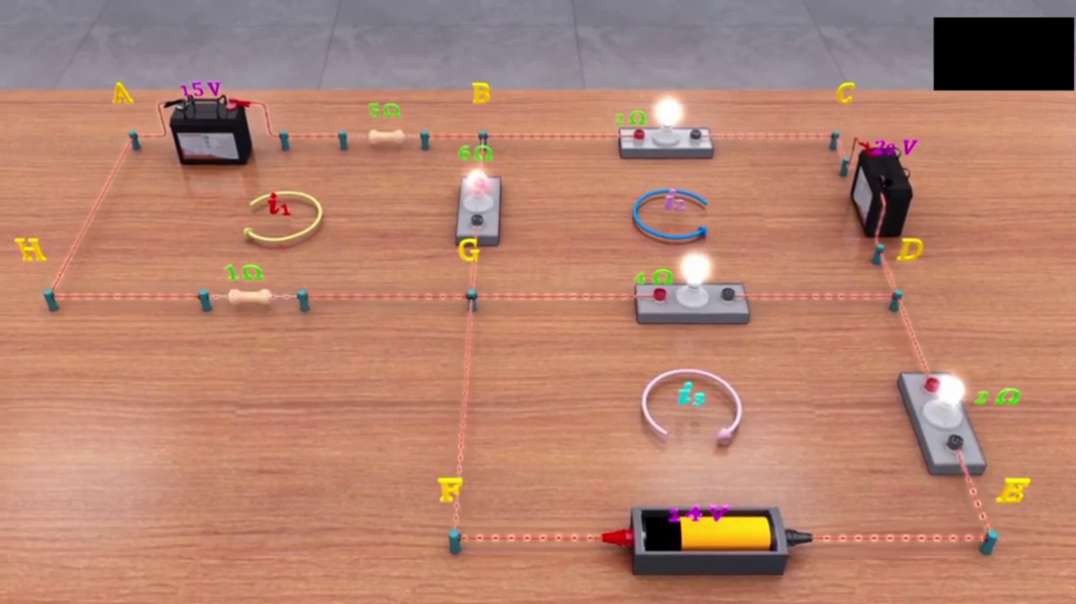
:
What is acceleration due the earth's gravity: Newton Laws
A free-falling object has an acceleration of 9.8 m/s/s, downward (on Earth). ... The numerical value for the acceleration of gravity is most accurately known as 9.8 m/s/s. There are slight variations in this numerical value (to the second decimal place) that are dependent primarily upon on altitude.
Is gravity 9.8 meters per second?
With algebra we can solve for the acceleration of a free falling object. The acceleration is constant and equal to the gravitational acceleration g which is 9.8 meters per square second at sea level on the Earth.
Why is gravity 9.81 ms 2?
Gravity (or the acceleration due to gravity) is 9.81 meters per second squared, on the surface of Earth, because of the size of Earth and the distance we are on its surface from its center. ... Throughout space, gravity actually is constant.
How 9.81 is calculated?
The acceleration g=F/m1 due to gravity on the Earth can be calculated by substituting the mass and radii of the Earth into the above equation and hence g= 9.81 m s-2.
Where is acceleration due to gravity is maximum?
The value of acceleration due to gravity is maximum at poles and minimum at equator.
At what height gravity is zero?
Near the surface of the Earth (sea level), gravity decreases with height such that linear extrapolation would give zero gravity at a height of one half of the Earth's radius - (9.8 m. s−2 per 3,200 km.)
Where is gravity the strongest?
Gravity is strongest at the Earth's surface, and its weakest at the Earth's core.