:
Cell Wall
Cell Wall Structure
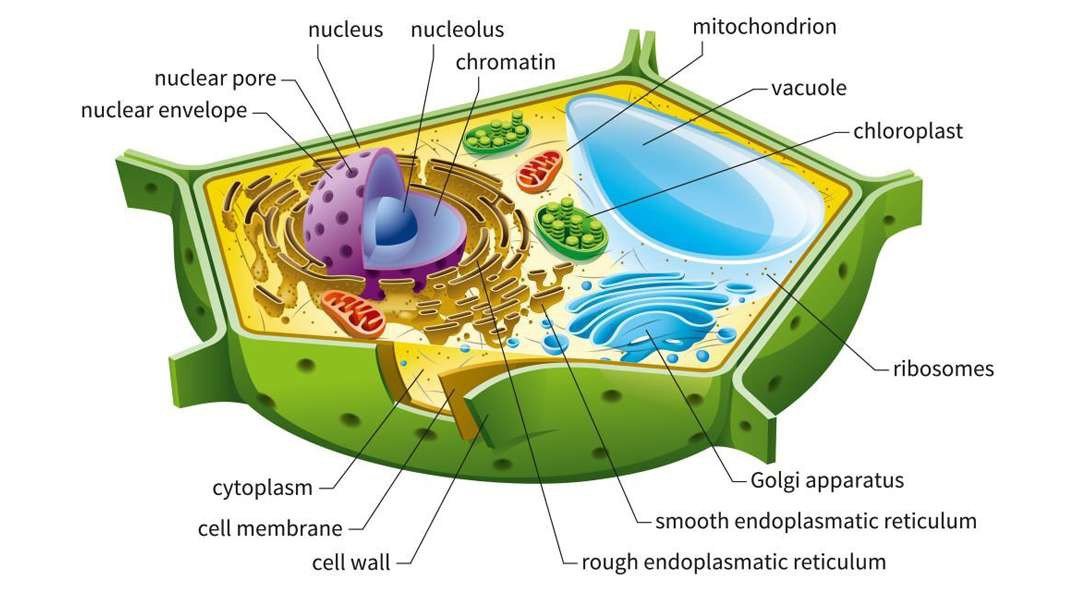
The cell wall is the outer covering of a cell, present adjacent to the cell membrane, which is also called the plasma membrane. As mentioned earlier, the cell wall is present in all plant cells, fungi, bacteria, algae, and some archaea. An animal cell is irregular in its shape and this is mainly due to the lack of cell walls in its cells. The compositions of the cell wall usually vary along with organisms.
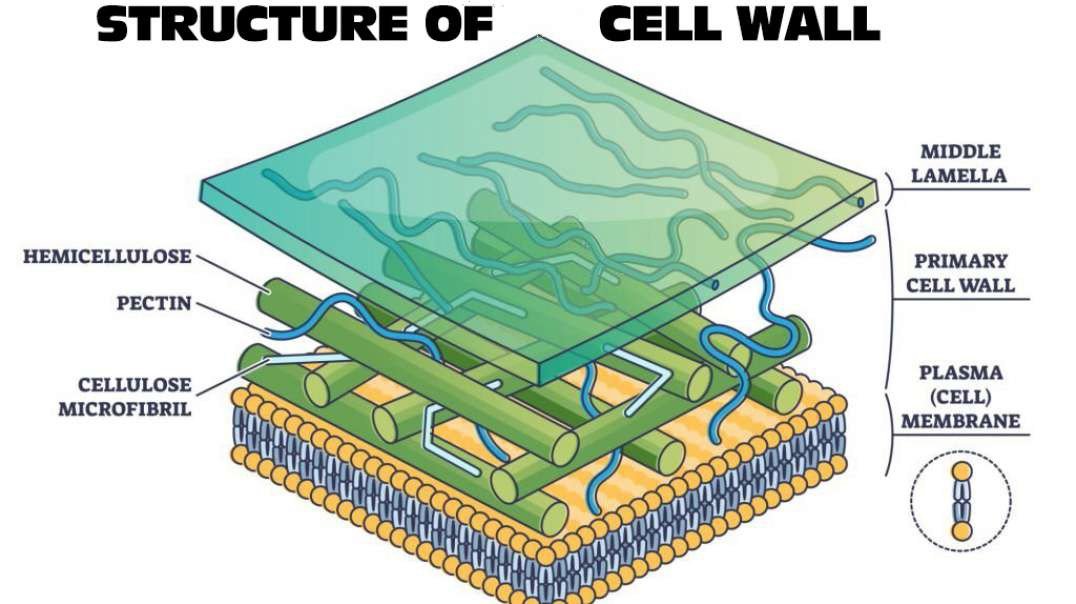
The plant cell wall is generally arranged in 3 layers and composed of carbohydrates, like pectin, cellulose, hemicellulose, and other smaller amounts of minerals, which form a network along with structural proteins to form the cell wall. The three major layers are:
Primary Cell Wall
The Middle Lamella
The Secondary Cell Wall
Primary Cell Wall
The primary cell is situated closest to the inside of the cell and is the first-formed cell wall. It is mainly made up of cellulose, allowing the wall to stretch for the purpose of growth. Several primary cells contain pectic polysaccharides and structural proteins. It is also comparatively permeable and thinner than the other layers.
Middle Lamella
The middle lamella is also the outermost layer and it acts as an interface between the other neighbouring cells and glues them together. This layer primarily consists of pectins. However, other substances such as lignin and proteins can also be found.
Secondary Cell Wall
The secondary cell wall is formed inside the primary cell wall once the cell is completely grown. Some types of cells (especially the cells of xylem tissues) consist of cellulose and lignin and these provide additional rigidity and waterproofing. Also, this layer provides the characteristic rectangular or square shape to a cell. It is also the thickest layer and permits permeability.
What is the Function of the Cell Wall
The cell wall is an integral component of the plant cell and it performs many essential functions. Following are some of the major cell wall functions observed:
The plant cell wall provides definite shape, strength, rigidity
It also provides protection against mechanical stress and physical shocks
It helps to control cell expansion due to the intake of water
Also helps in preventing water loss from the cell
It is responsible for transporting substances between and across the cell
It acts as a barrier between the interior cellular components and the external environment