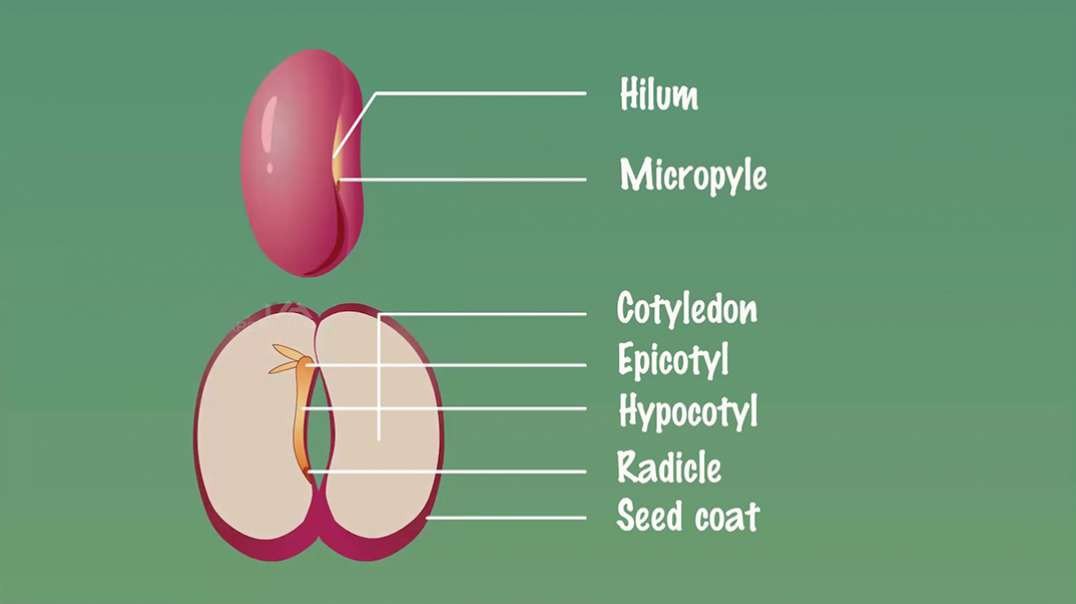
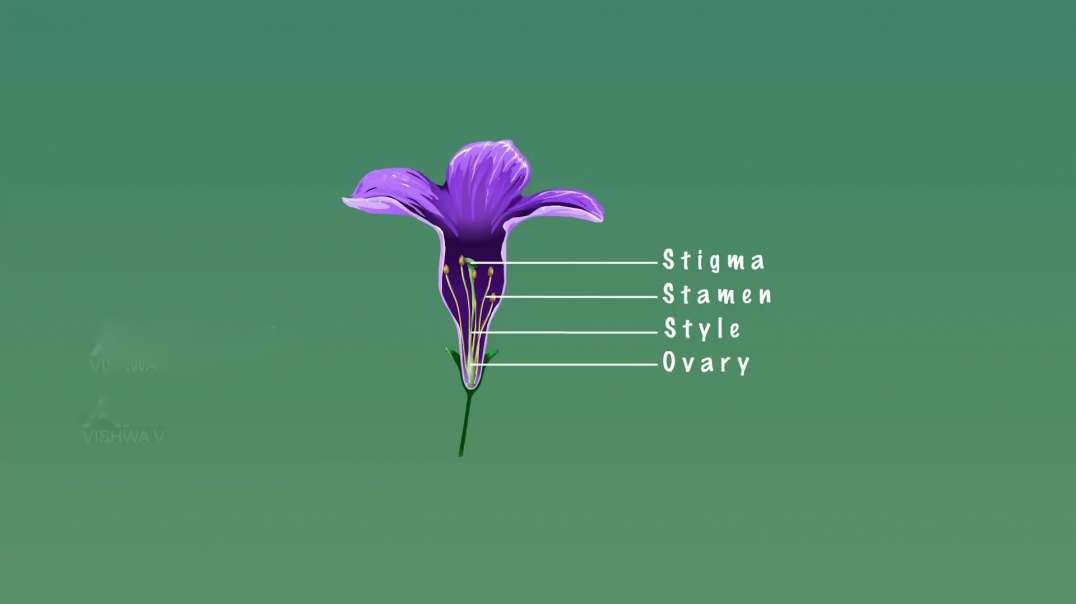
:
Characteristics of Dicot and Monocot Stem and Root
Characteristics of Dicot and Monocot Stem and Root :-
Stems and roots of plants are made up of different types of tissues. These tissues form different layers in the composition of stems and roots. Monocot and dicot stems differ in the arrangement of their vascular system. Monocot stems have scattered vascular bundles. Dicot stems have their vascular bundles in a ring arrangement. Monocot stems have most of their vascular bundles near the outside edge of the stem. The bundles are surrounded by large parenchyma in the cortexregion. There is no pith region in monocots. Dicot stems have bundles in a ring surrounding parenchyma cells in a pith region. Between the bundles and the epidermis are smaller (as compared to the pith) parenchyma cells making up the cortex region.
Monocot roots, interestingly, have their vascular bundles arranged in a ring. Dicot roots have their xylem in the center of the root and phloem outside the xylem. A carrot is an example of a dicot root.
This video explains how to prepare temporary stained glycerine mounts of transverse sections of the stem and root of Dicot and Monocot plants.