:
Facilitated Diffusion: Detailed Animation
Some molecules, for example, highly charged molecules such as sodium ions, or larger molecules like glucose, cannot cross a membrane by simple diffusion. This is because they are too hydrophilic to penetrate the non-polar central region of the lipid bilayer.
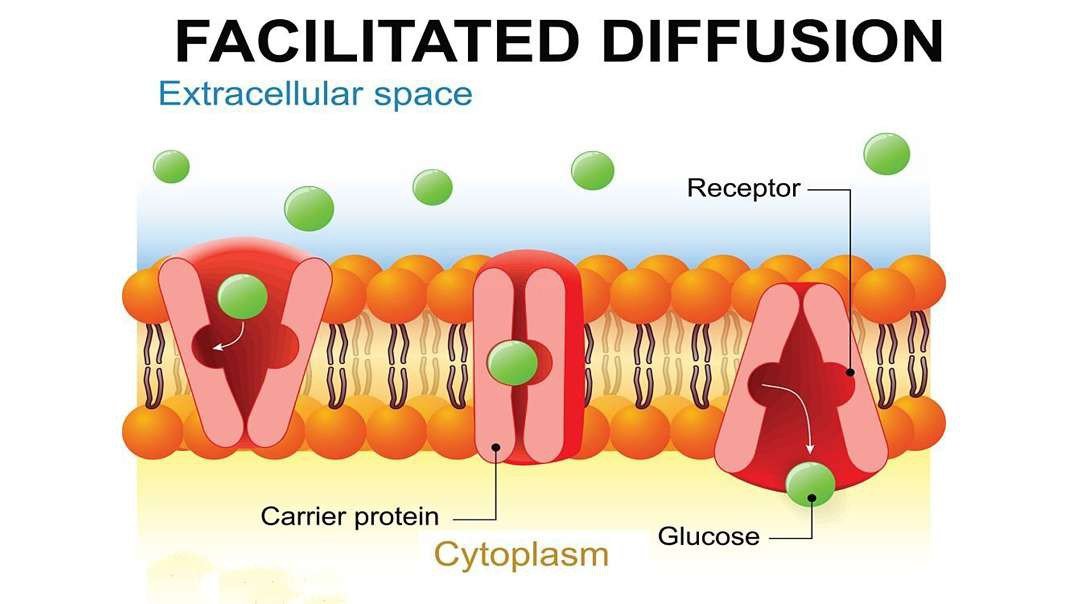
The movement of these substances across a plasma membrane, therefore, requires the presence of an ion channel or carrier protein within the membrane itself to facilitate diffusion.
There are two main types of facilitated diffusion: channel-mediated facilitated diffusion and carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion.
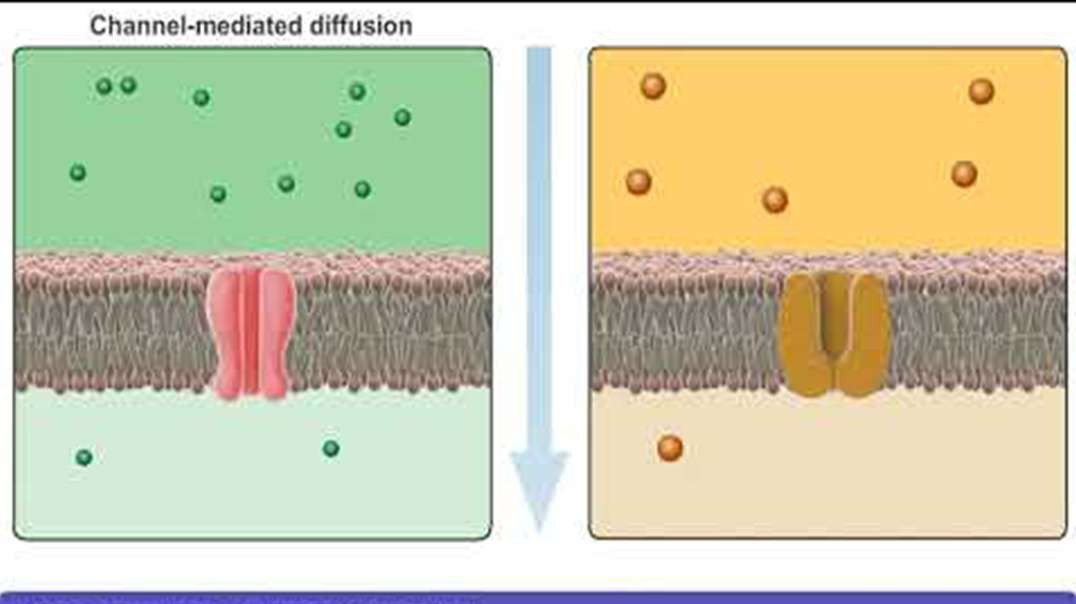
Channel-mediated facilitated diffusion
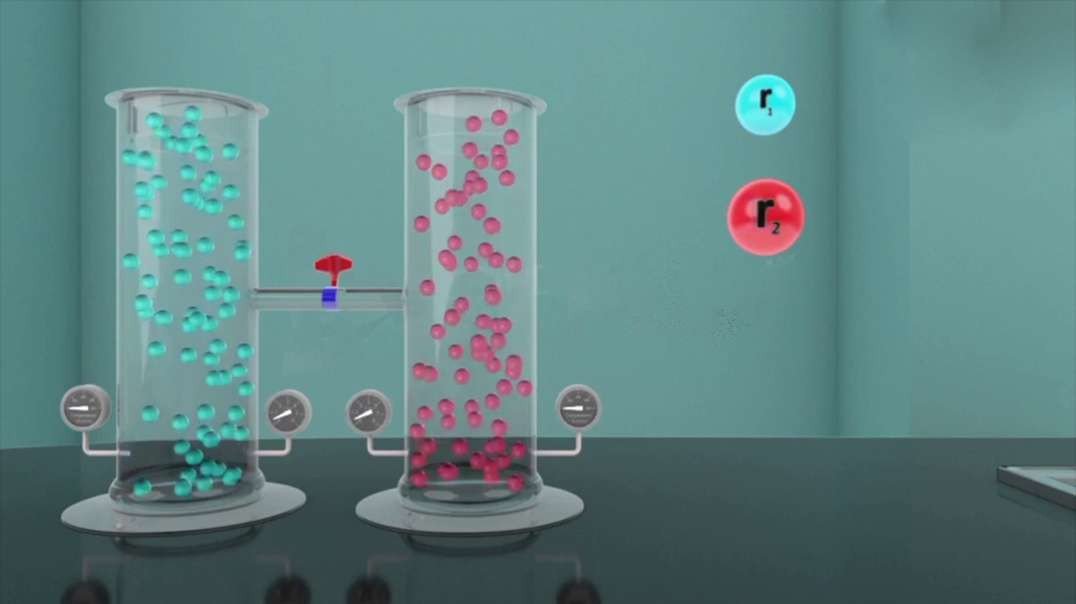
During channel-mediated facilitated diffusion, solute molecules diffuse down their concentration gradient, from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low solute concentration, by passing through an ion channel within the plasma membrane.
Ion channels are often very selective, only permitting the passage of a single type of ion. These channels may also be gated, only permitting diffusion to occur when they are open.
Example The movement of sodium ions required for neuronal activity in the brain.
Substances involved Highly charged molecules
(e.g., sodium, potassium, chloride, and calcium ions)
Rate limited by The rate of channel-mediated diffusion is determined and limited by the number of ion channels in the plasma membrane and the steepness (amount of difference) of a substance's electrochemical gradient.
Carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion
During carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion, solute molecules diffuse down their concentration gradient, from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low solute concentration, by binding to a carrier protein within the plasma membrane. The carrier protein undergoes a conformational change, which deposits the solute molecule on the opposite side of the membrane.
Example The uptake of glucose from the blood into liver cells.
Substances involved Large, polar, lipid-insoluble molecules
(e.g., glucose and amino acids).
Rate limited by The rate of carrier-mediated diffusion is determined and limited by the number of available carrier proteins in the plasma membrane and the steepness of a substance's electrochemical gradient.