:
Protein synthesis : translation(A more detailed and compiled form)
What is translation DNA?
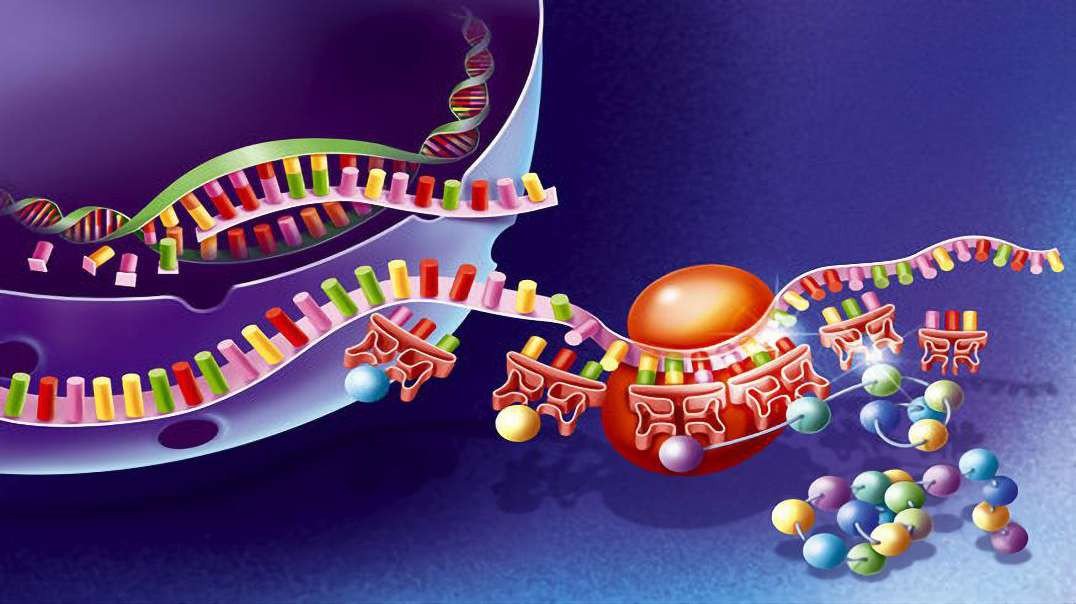
Translation is the process that takes the information passed from DNA as messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds. The ribosome is the site of this action, just as RNA polymerase was the site of mRNA synthesis.
People also ask, what is the purpose of translation in DNA?
Translation is the process that takes the information passed from DNA as messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds. It is essentially a translation from one code (nucleotide sequence) to another code (amino acid sequence).
Likewise, what is the process of translation? Translation is the process of translating the sequence of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule to a sequence of amino acids during protein synthesis. The genetic code describes the relationship between the sequence of base pairs in a gene and the corresponding amino acid sequence that it encodes.
Accordingly, what is translation of DNA definition?
DNA translation is the term used to describe the process of protein synthesis by ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum. tRNAs carry particular amino acids, which are linked together by the ribosome. In this process, the mRNA is decoded to produce a specific amino acid chain, known as a polypeptide.
What is the end product of translation in DNA?
proteins