:
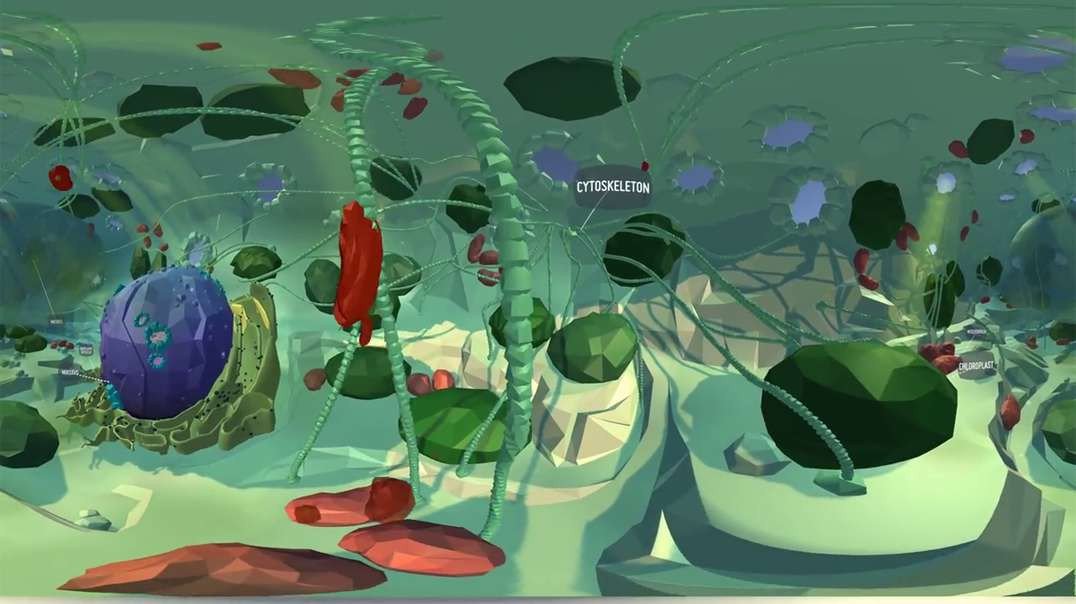
Plant Cell and its organelles simulation
INTRODUCTION
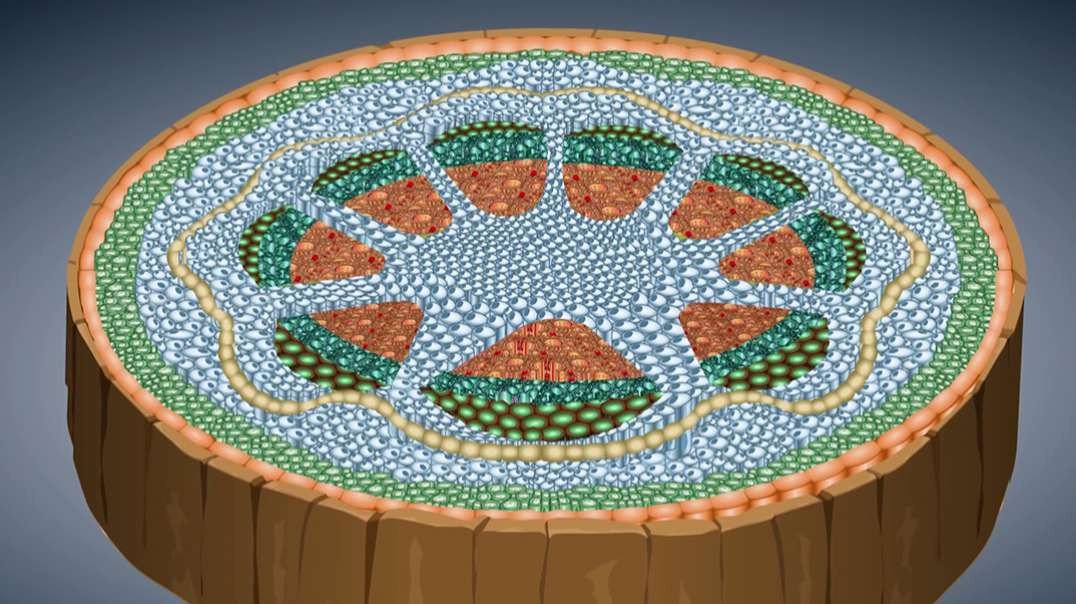
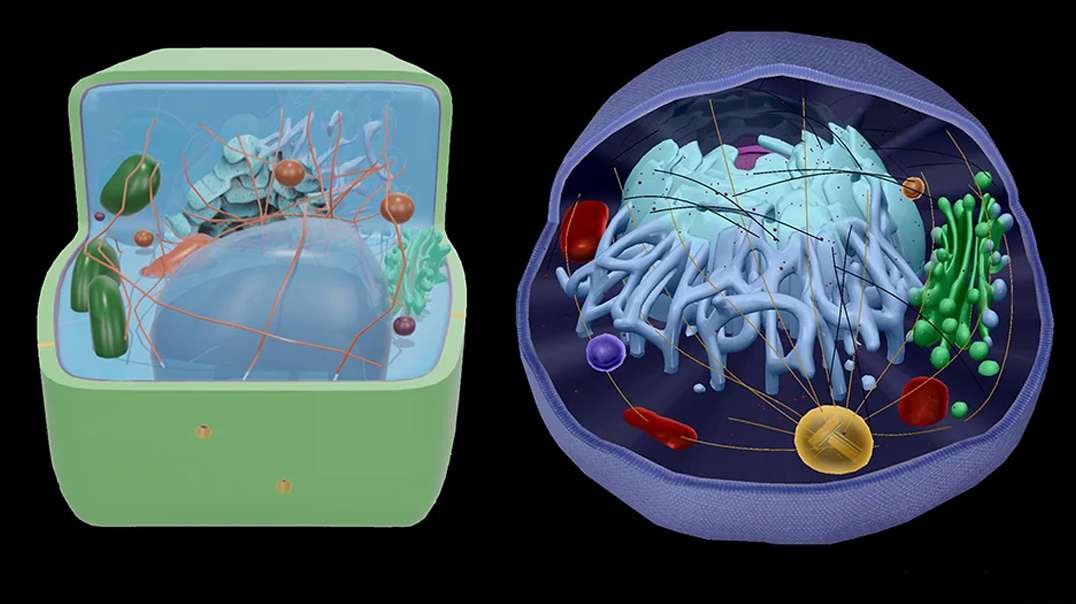
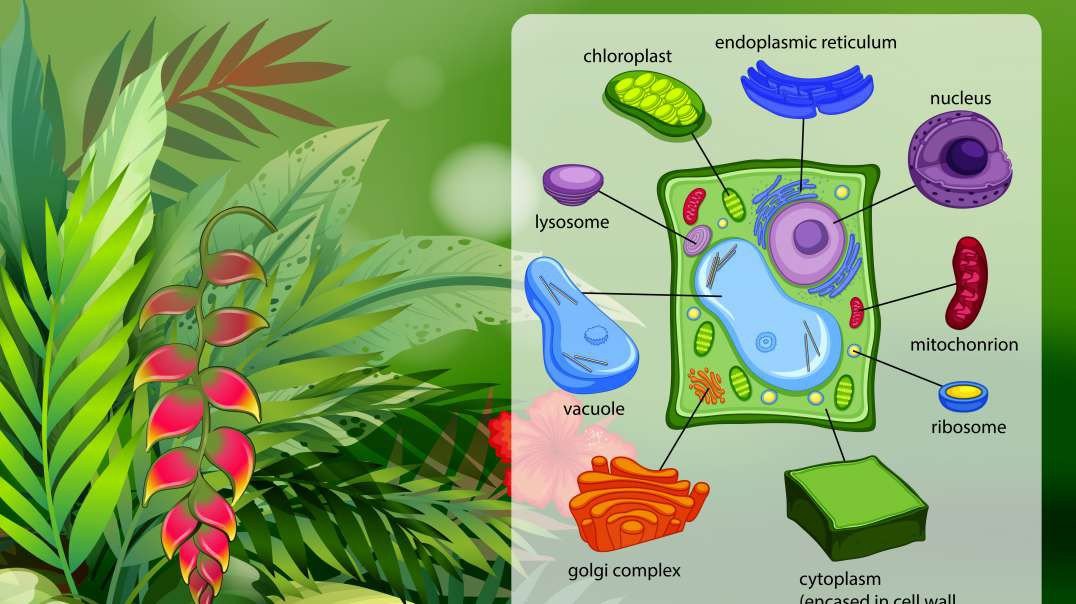
The plant cell has 18 different types of organelles¹ with specialized functions.
ORGANELLES OF THE PLANT CELL AND THEIR FUNCTION
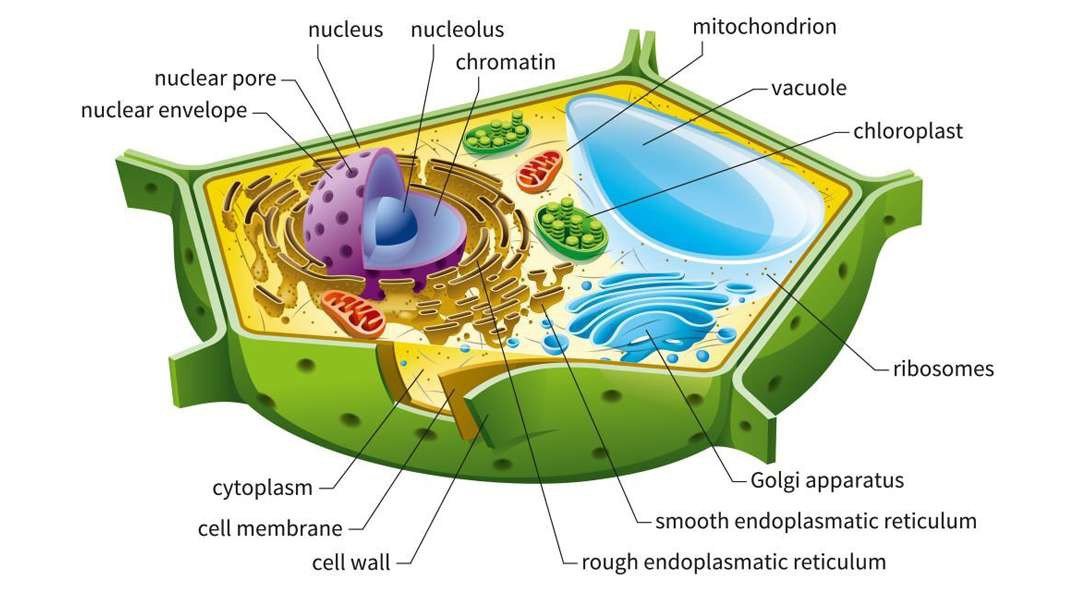
Plasma membrane: Separates the cell from its environment; regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
Mitochondria: Oxidize ATP.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER): Protein synthesis.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER): Synthesis of lipids; Drug metabolism.
Nuclear envelope: Segregates chromatin (DNA + Protein) from the cytoplasm.
Nucleolus: Synthesis of ribosomal RNA.
Nucleus: Contains the genes (chromatin).
Golgi Complex: Processes, packages, and distributes proteins to other organelles for export.
Cell wall: It confers shape and rigidity; protects the cell from osmotic swelling.
Cytoskeleton: Structural support of cells; facilitates the movement of organelles.
Glioxisome: Contains the enzymes of the glyoxylate cycle.
Ribosomes: Protein synthesis.
Plasmodesmata: They allow the passage between two vegetal cells.
Vacuole: Degrades and recycles macromolecules and stores metabolites.
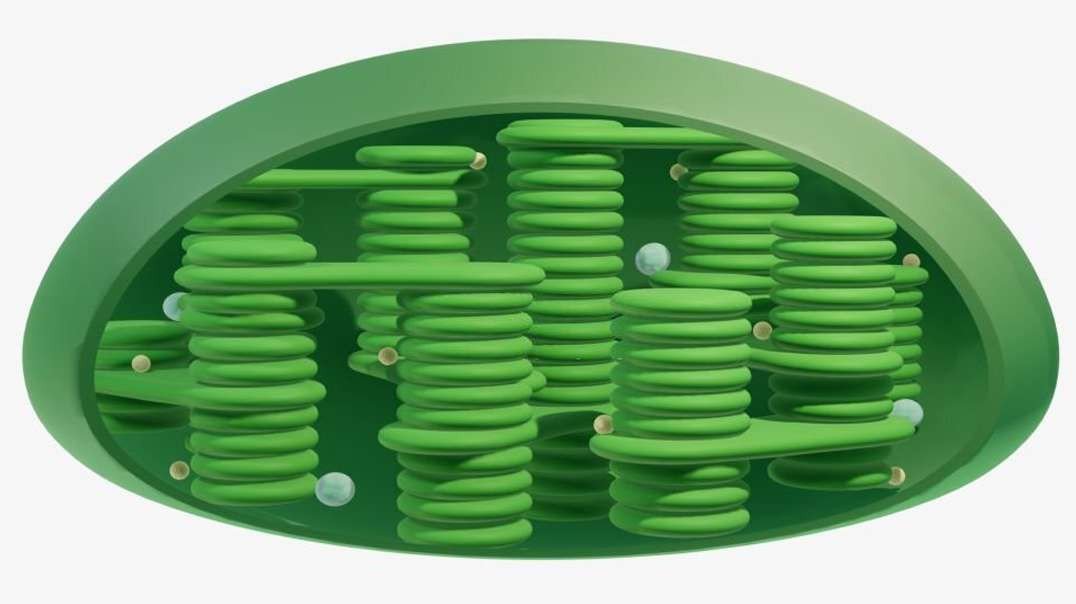
Thylakoids: They synthesize ATP through light energy.
Starch grain: Temporary carbohydrate store, photosynthesis producer.
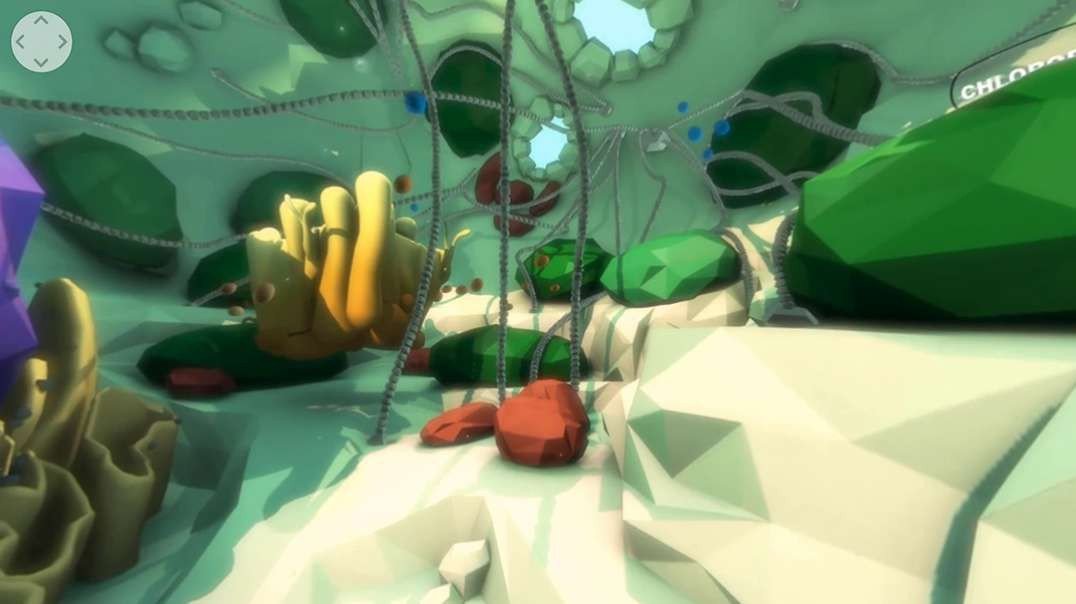
Chloroplast: Stores solar energy, and produces ATP and carbohydrates.
Peroxisome: They are involved in the catabolism of fatty acids.