:
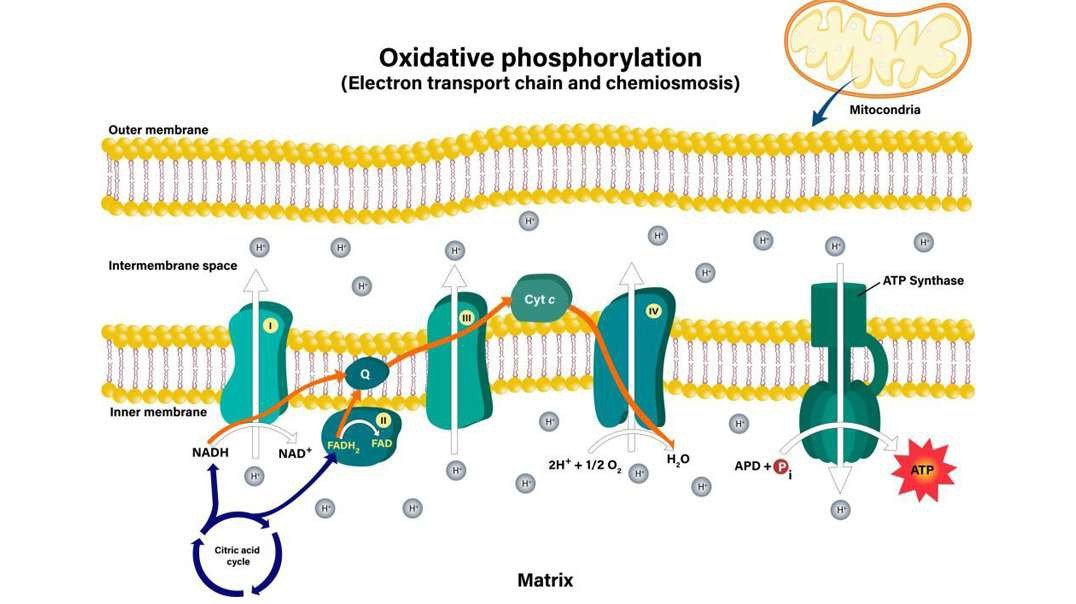
The Electron Transport Chain (Aerobic Respiration Stage 4)
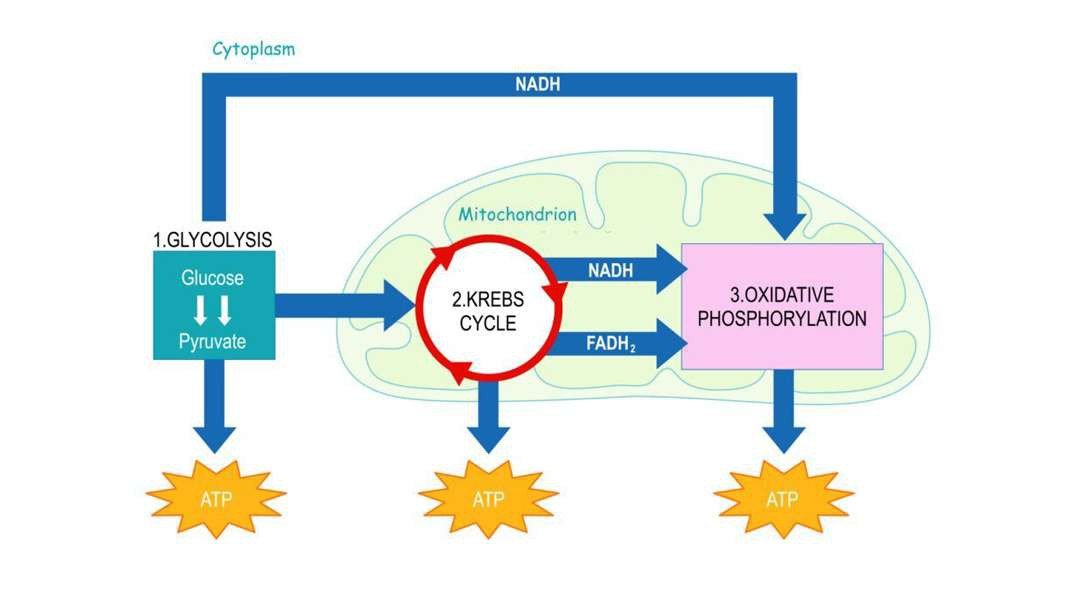
Aerobic Respiration: Stage Four: Electron Transport Chain
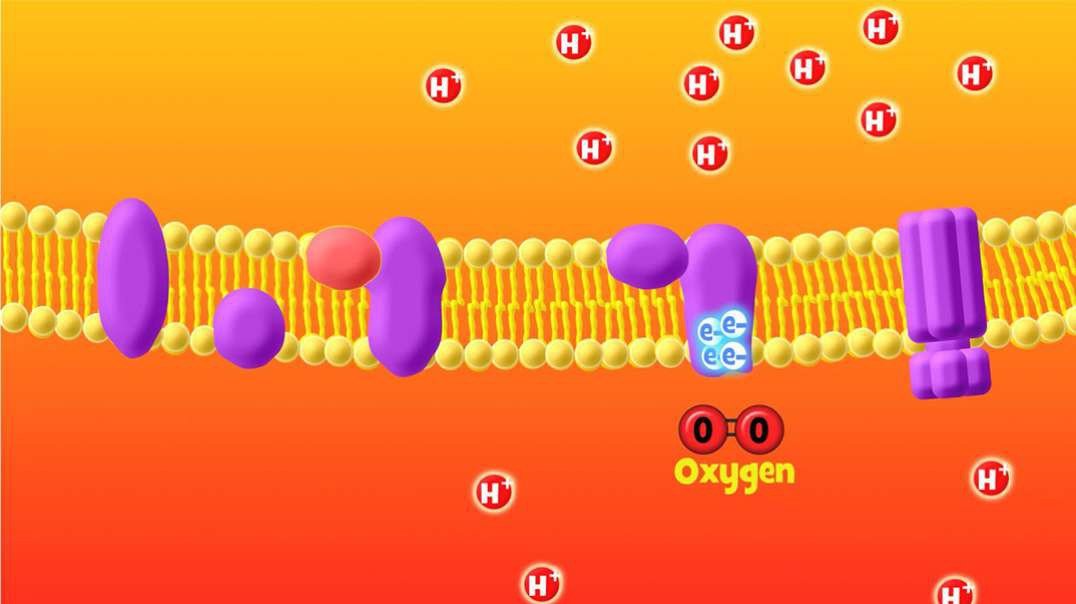
All the reduced electron carriers now enter into this step, the electron transport chain. In this step, the energetic electrons carried by electron carriers like NADH are utilized for the production of a large amount of ATP.
Electron transport chains are collectively made up of membrane-embedded proteins and organic molecules. The electronic transport chain components are found in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes, whereas in eukaryotes, many copies of these molecules are found in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The electron transport chain contains proteins such as Fd (ferredoxin), PQ (plastoquinone), Cyt C (cytochrome C), Q (ubiquinone), and PC (plastocyanin). The enzyme NADP reductase is also present. It is important in the reduction of an electron acceptor molecule and in the generation of NADPH.
While travelling of electrons through the chain, it enters into a lower energy level from a higher energy level. It means it moves from less electron-hungry molecules to more electron-hungry molecules. Hence, this type of transfer of electron is an example of downhill electron transfer. The above-mentioned different protein complexes use the released energy (released during electron transfer) and that turn out into pumping of the proton from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. This is particularly responsible for forming a proton gradient.
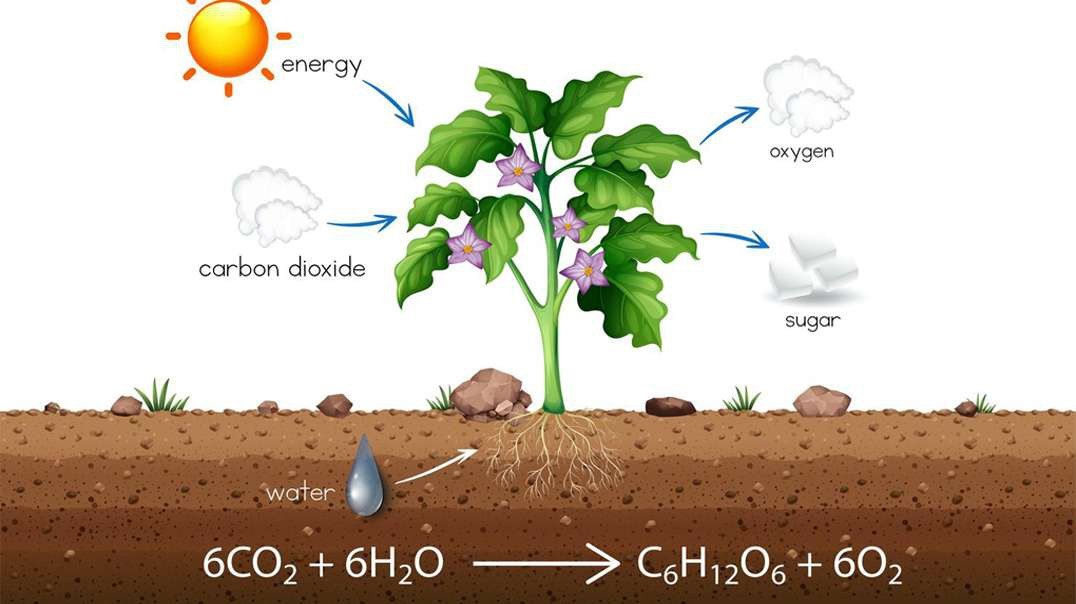
The reaction like pyruvate oxidation, the reaction of the Krebs cycle, and the production of ATP by electron transport chains take place within many forms of bacteria, and inside the mitochondria of all eukaryotes. (Note- According to researchers, mitochondria are thought to have evolved from bacteria. As you know, plants and algae are photosynthetic and they are able to produce ATP by using sunlight. However, these photosynthetic organisms are also capable of producing ATP by aerobic respiration just like animals and other non-photosynthetic eukaryotes do.
Summary of Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration is the aerobic catabolism of carbohydrate to carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
The overall aerobic respiration can be mentioned by following chemical reaction.
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O
This type of cellular respiration is seen in aerobes and facultative anaerobes.
Aerobic respiration involves four stages- glycolysis, a transition reaction that forms acetyl-CoA, the Krebs cycle, and an electron transport chain.